OSHA Fire Extinguisher Clearance Requirements: Everything You Need To Know
- May 30, 2024
- 9 Min Read

- Fire extinguishers need monthly checks and yearly maintenance.
- A full inspection is required at 6 years, with hydrostatic testing at 12.
- Employees must be trained every year when hired.
- Extinguishers must be easy to reach and placed wisely.
- Following OSHA rules keeps workplaces safe.
According to the US Fire Administration, nearly 1,000 deaths have already occurred due to fires in 2024 as of the end of this month. The one thing most of these situations have in common is hazardous materials in the environment that cause the fire.
Although we understand the seriousness that fire damage can cause, sometimes we don’t take suitable measures to ensure that we are protected from it. Proper fire safety and compliance can easily prevent the chance of an out-of-control fire causing any injury or death.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) is a governmental organization that protects occupational workers from harmful working conditions that may endanger their health and lives. To do this, OSHA enforces specific standards and policies that everyone must follow.
In this piece, we’ll examine OSHA standards for fire extinguishers, including placement, mounting, distancing, and more.
Table of Contents
Make inspections easy—use our templates to spot risks, act fast, and get the job done right!

Understanding OSHAs' Criteria
Fire extinguishers are an essential tool in your arsenal of fire safety equipment because they are often the first solution to preventing a minor fire from worsening. The 1910.157 Standard is the main guideline presented by OSHA for the clearance and positioning requirements of portable fire extinguishers.
Most of us have seen plenty of fire extinguishers in different environments but have never had the need to use one, which is good. However, the placement of these fire extinguishers, making sure that they are accessible to everyone in an emergency, is a real challenge.
OSHA has established specific standards for businesses to follow when handling and placing fire extinguishers. These rules have been made after considering the needs of people in such environments if a fire is to occur: their response time, the best location for quick access, minimum spreading of the fire, and similar points for the safety of individuals against a fire.
Here are the general requirements of the 1910.157 Standard of OSHA for a portable fire extinguisher,
1910.157(c)(1)
The employer shall provide portable fire extinguishers and mount, locate, and identify them so that they are readily accessible to employees without posing a possible injury.
1910.157(c)(2)
Only approved portable fire extinguishers shall be used to meet the requirements of this section.
1910.157(c)(3)
The employer shall not provide or make portable fire extinguishers using carbon tetrachloride or chlorobromomethane extinguishing agents available in the workplace.
1910.157(c)(4)
The employer shall ensure that portable fire extinguishers are maintained in a fully charged and operable condition and kept in their designated places at all times except during use.
1910.157(c)(5)
The employer shall remove from service all soldered or riveted shell self-generating soda acid or self-generating foam or gas cartridge water type portable fire extinguishers which are operated by inverting the extinguisher to rupture the cartridge or to initiate an uncontrollable pressure-generating chemical reaction to expel the agent.
Source: 1910.157 Standard of OSHA
Get this FREE fire extinguisher NFPA-compliant form and keep your extinguishers ready-to-use when needed!
Types of Fire Extinguishers
Some fires can be caused by specific materials, which can be impervious to some extinguishers with different extinguishing agents. Hence, various fire extinguishers for the different types of fire hazards need to be put out. They are divided into different classes, and each class has its group of materials for which that particular extinguisher is used.
The requirements for placement of fire extinguishers in the correct positions also depend on the class of the fire extinguisher and the hazards it is protecting against. Hence, it is imperative to understand these different categories and place them according to the policies provided.
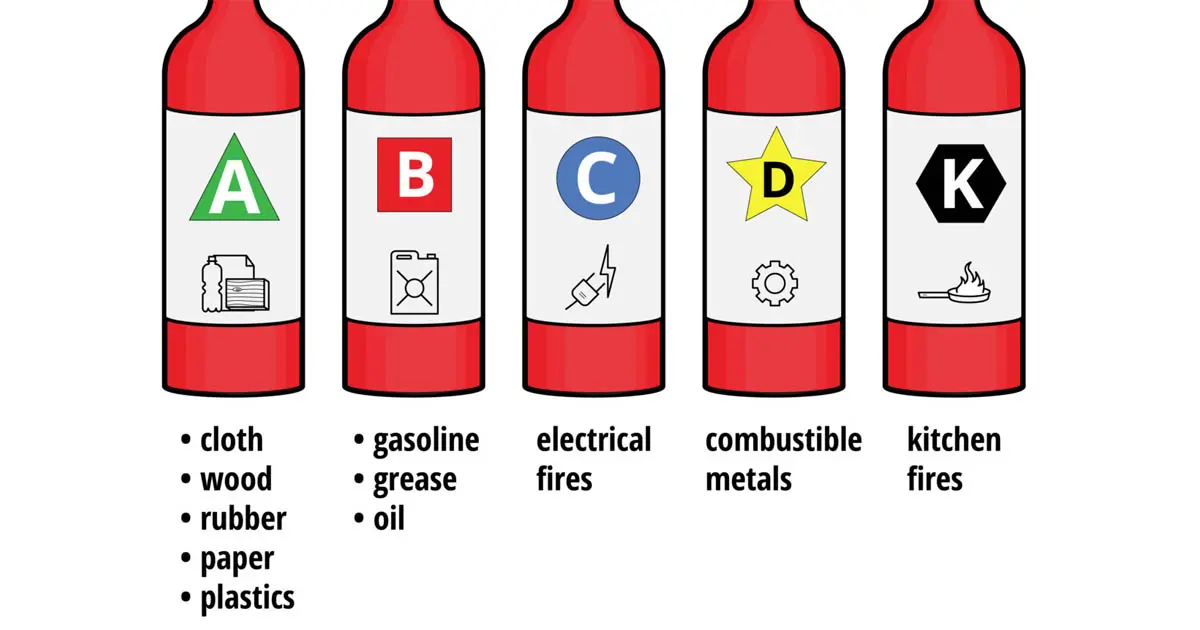
Source: Fire Extinguisher Types
| Class of Fire | Characteristics | Type of Extinguisher Needed |
| A | Solids (paper, wood, cardboard, building materials, and other solid combustible materials) | Water, dry chemical, clean agent |
| B | Liquids (cleaning fluid, fuel, paint, etc.) or gases (natural gas, LPG, etc.) | Carbon dioxide, dry chemical, clean agent |
| C | Electrical equipment | Carbon dioxide, dry chemical, clean agent. Not water under any circumstances. |
| D | Flammable metals | Dry powder and specialist suppression depending on the metal |
| K | Cooking fats and oils | Wet chemical |
OSHA Fire Extinguisher Placement and Mounting
Placement Requirements
According to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), it is vital to ensure that extinguishers are accessible and properly placed so that employees and any impaired individual can instantly see and use these resources. Here are some specific guidelines to follow for this,
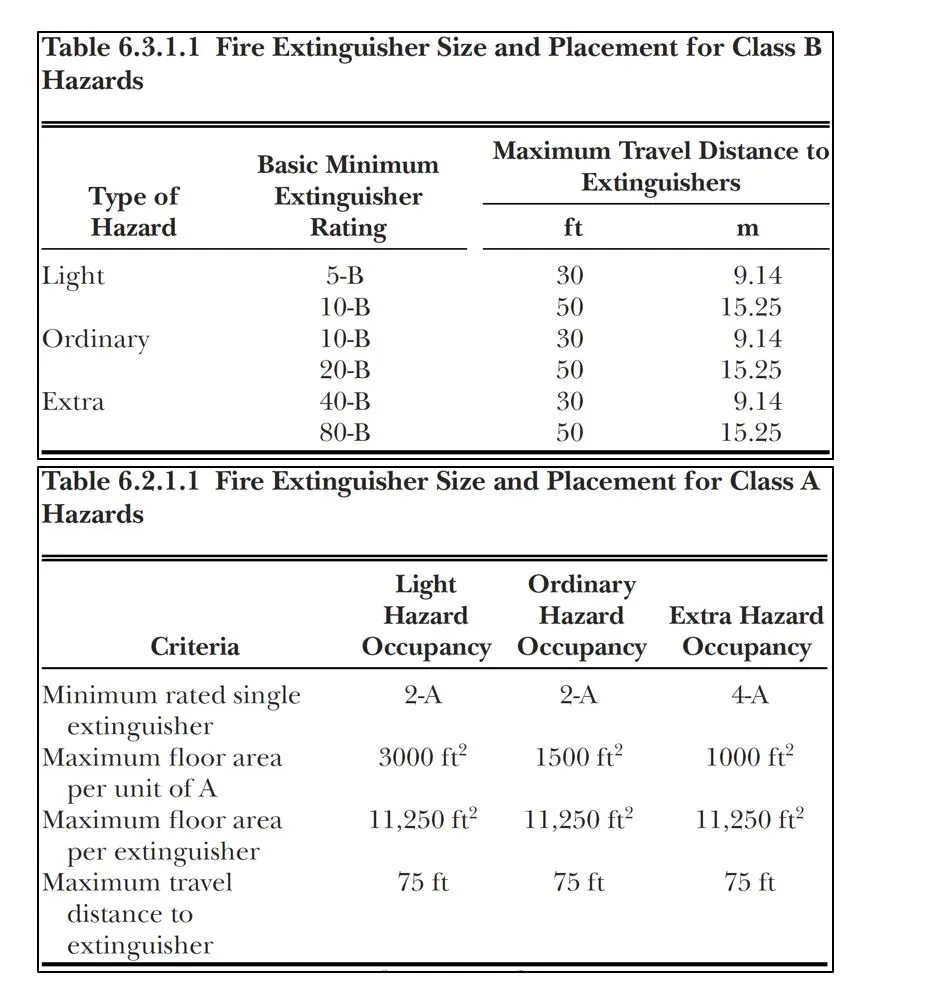
| Class of Fire Risk | Placement of Extinguishers |
| A | NFPA recommends one 2-A fire extinguisher for every 3,000 square feet. OSHA requires employees to have access to an extinguisher within 75 feet. |
| B | Employees should have access to a fire extinguisher within either 30 or 50 feet, depending on the hazard in question and the rating of the extinguisher (see below). |
| C | As a C class extinguisher can only earn this rating if it has already gained an A, B, or AB rating and does not conduct electricity, the placement depends on the class A or B hazards in the workplace. |
| ABC | Dependent on the hazards in your workplace, and whether they fall into class A or B. |
| D | Placed not more than 75 feet from the hazardous metal. |
| K | Placed not more than 30 feet from the fire hazard. |
The extinguisher must be freely placed and clear of any obstructive material.
During a fire hazard, extinguisher spacing light is essential to identify the location and access to an extinguisher quickly.
Some physical indications, like painted lines or arrows, must highlight a minimum clearance of about 36” around the extinguisher area.
Uniformly spaced standpipe systems and ensuring that hose stations connected in parallel are active prevent fire extinguishers from being blocked by obstructions.
It should never be used as a hanger for other materials, like electrical cords, emergency clothing, office materials, or anything else.
Training Of Employees

Safe and inspected extinguisher is a boon in times of need. Stay compliant easily with this free checklist!
These regulations are designed to provide a proactive solution for workers in a building during a fire emergency. However, even the correct placement is not always enough. This is why employee training on what to do during such a situation is essential to any business’s fire emergency action plan.
OSHA has provided businesses with guidelines they need to follow. This can help them educate their employees on how to properly distribute portable fire extinguishers and what they need to know to initiate proper safety measures during fire hazards. Here are the training and education requirements of the 1910.157 Standard,
1910.157(g)(1)
Where the employer has provided portable fire extinguishers for employee use in the workplace, the employer should also provide an educational program to familiarize employees with the general principles of fire extinguisher use and the hazards involved with incipient stage fire fighting.
1910.157(g)(2)
The employer should provide the education required in paragraph (g)(1) of this section upon initial employment and at least annually thereafter.
1910.157(g)(3)
The employer should provide employees designated to use fire fighting equipment as part of an emergency action plan with training in using the appropriate equipment.
1910.157(g)(4)
The employer shall provide the training required in paragraph (g)(3) of this section upon initial assignment to the designated group of employees and at least annually thereafter.
Inspecting and Maintaining Extinguishers
The placement and positioning of a fire extinguisher are essential, but none of them will matter if the extinguisher doesn’t work when needed. That’s why the maintenance of fire extinguishers is another integral component in the architecture of fire safety.
Maintenance of fire extinguishers can include different procedures according to the time intervals in which the inspections need to be done. These fire inspections and frequency are a principal component of fire safety regulations mandated by the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association).
Like OSHA, the NFPA also has specific guidelines regarding what needs to be done during an inspection, how to maintain portable fire extinguishers, where to provide portable fire extinguishers, the minimum requirements for using a fire extinguisher, and penalties for not following the procedures.
Inspections can be done,
Monthly: These are primarily visual inspections done by anyone with general knowledge about maintaining fire extinguishers.
Annually: Annual inspections are a more detailed look at the health and functioning of a fire extinguisher.
6-Year Inspection: This inspection focuses on a complete external examination of the extinguisher body and its physical working components every six years.
12-Year Inspection: Every 12 years, this inspection is also an external checking of an extinguisher but with more focus on internally checking the tool. The extinguishing agent is refilled, and the entire system undergoes hydrostatic testing.
Know which fire extinguisher works best for each fire. Learn requirements based on NFPA10 And U.S. Fire Codes with this quick FREE step-by-step guide.
Conclusion
If you’re interested, we’ve written a more comprehensive and detailed article about the requirements of each inspection and maintenance procedure in the official books. Give it a read to see what is required to maintain fire extinguishers according to the NFPA guidelines. Also, if you need more facts about fire extinguishers, fire inspections, or general fire safety tips, you can check out our collection of 100+ articles that have all the info you need.

Get Insights Delivered Straight
To Your Inbox!
Related Reading
Why Your Field Software Management Software Needs QuickBooks Integration
ZenTrades Why Your Field Service Management Software Needs QuickBooks Integration Read More Request Demo...
Read MoreZenTrades How To Manage Electrical Service Agreements Like...
Read MoreZenTrades The Best 5 Jobber Alternatives In 2023...
Read More



